
Knee pain is a common symptom signaling about the contrasts in the body – the emergence of the disease of the joints or simply the increased load on the legs.
It is difficult to find a person, never experiencing the pain in the knees, in a particular period of life. Discomfort, clicking or pain of variable intensity in the joints of the knee occur both in adults as in children because of the multitude of reasons. The older becomes in a person, the greater is the probability of the occurrence of various diseases, the first sign of that is the pain in the knees. This happens due to the age of the body: the deceleration of the processes of change, wear and tear of the cartilage of the joints, the adhesion of other problems in the motor apparatus of the apparatus, vessels, nerves.
Due to the complexity of the structure anatmica, the amount of structures and the important loads, in times of overload, the knee joints are very vulnerable. Damage of any element of the structure, for example, bags synovial, leads to the violation of the motor function of the knee and, consequently, the pain syndrome. The ligaments and meniscus lenses are considered the most vulnerable, that there are in the 80-85% of the cases.
The anatomical structure of the knee
The knee is composed of the knee, the distal end of the femur, with two condyles and bajocóndilos, tibial tubular bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, ligamentous apparatus, of the kneecap (patella), the joint capsules and menisci.
The knee joint is one of the major joints of the body. Up on he thigh. Joint guided to the surface of your lateral (outer) and middle (internal) condyles connect with the patella and the tibia bone. Meniscus lenses, which represent connective tissue cartilage, serve as shock absorbers of the joint. Thanks to them occurs the distribution of the weight of a person in tibial plateau and increases the stability of the joint. Thin, double-head, paliperidonesee and other muscles synchronized capsule-ligamentous structure, providing the motor activity of the knee.
Elements of the knee joint and connected to each other by many ligaments. The inside of the joint, there are two crosses posterior ligament and front. Podmyshalsky bedernau the bones are connected with the fibula and tibia bones collateral ligaments. Bar cushion knee ligament located on the posterior part of the bursa of the knee. Of the series of the sockets, distinguish primary – synovial capsule, not the communication with the joint. The blood supply of the elements of the knee is performed thanks to the network of the blood vessels, and the innervation – nerve fibers.
The causes of pain in the knees
There are many causes of pain in the joints of the knees, which can be divided into several groups.
Traumatic defeat of the elements of the knee:
- A knee injury. As a result of the rupture of blood vessels produces local bleeding in the soft tissues of the joint. The redness, the swelling, the defeat of the nerve endings causes pain, difficulty of movement.
- Complete or partial rupture of the ligaments. Often diagnosed partial violation of the integrity of the internal lateral ligament, arises from an excess of eversion of the leg outward.
Outside, the ligament breaks less in comparison with the interior. This occurs due to the strong deviation of the leg towards the interior, when the exposure legs for example. The gap torn ligaments, inevitably accompanied by a hemarthrosis.
A complete rupture of both ligaments is often combined with the damage of the joint of bags, tearing internal meniscus. This injury leads to excessive motion of the knee, which is accompanied by severe pain, whose intensity depends on the degree of rupture.
- Hemarthrosis of the knee – to spill blood in the cavity of the joint. It's traumatic and non-traumatic nature. The traumatic hemarthrosis occurs when the jumps of the meniscus, complete or incomplete of the jumps of the ligaments, guided intra-articular fractures, contusions knee area. Non-traumatic option is one of the symptoms of diseases characterized increased fragility of the walls of the vessels or of the violation of the coagulation system of the blood. These include hemophilia, scurvy, the severe forms of hemorrhagic diathesis. Has accumulated in the joint cavity from the blood, tightens the tissue, altering the circulation of the blood in them. Special pigment – hemosiderin–, affects the ligaments, hyaline cartilage, synovial lining of the bag, resulting in the loss of its elasticity. The result of the defeat of the joint bursa is the swelling of the intestinal villi and to enhance the production of joint fluid. The result of repeated hemorrhage becomes in muscular dystrophy and destruction of the joint.
- The knee miniscope – the violation of the integrity of the menisci of the knee. When side-way is damaged outer meniscus, when the medial internal. It is one of the most frequent, but difficult-to-diagnose knee injuries. In the area of risk of the disease are found here not only the athletes who engage in intense training sessions, but also the common people. The rupture of the meniscus can occur by the strong increase in unusual movement by turning the torso, the exposure of the leg, a strong blow to the knee.
- A dislocation of the patella – pathologic dislocation of the patella. The injury is diagnosed in no more than 0.7% of the cases of the total number of dislocations. It occurs most frequently outside of a dislocation of less – internal, very rarely – vertical or torsional. The incomplete dislocacin of the knee cup is defined on the lateral (outside) condyles, on the full – on the outside of the lateral condyle.
- Open or closed fractures of the knee, the upper part of the bones of the leg or bottom of the division bedernau bones. These lesions often are combined with the defeat of the soft tissues of the knee, causing a massive hemorrhage excessive mobility in the area of the tribe, their deformation.
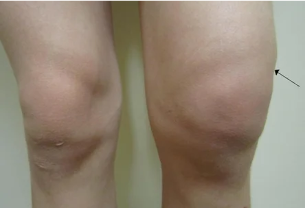
Inflammatory and atrophic disease joint guidance of the elements of the knee:
- Arthritis – inflammatory of the defeat of the knee joint. A similar mechanism, the development of the pathology is occurs when the osteoarthritis, the disease behtereva, rheumatoid arthritis, gout (with deposit of urate in the joints).
- Osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) with the defeat of the knee non-inflammatory nature, affecting all of its structure and give rise to severe degenerative changes.
- Bursitis of the synovial inflammation of the pouch cause pain when flexion-extensor movements of the knee.
- Parasynovitis of the tendons of the knee – inflammation of the capsule goose of the leg, the tendons of the knee, as well as the muscles and ligaments that surround the joint. When this pain occurs primarily during the descent of the stairs, especially with a very heavy load, and is focused on the inner surface of the knee.
- The chondropathy of the patella tendon – degenerate-necrotic changes in the cartilage of the joint (posterior) surface of the patella. The degree of destruction that can be different: plots slight softening up the cracks and the total of the abrasion.
- Chondromatous – to-severe chronic illness due to the dysplastic process the islets of the regeneracin of the plots of the membrane of the joint shell in the cartilage – gondrom. Does not rule out the ossification of individual cartilage tel.
- A baker's cyst – the formation of a dense elastic rounded in the carcinogenesis of education in podkolennoy the pit, located on the opposite side of the patella. A cyst is clearly visible in the flattened state of the knee. Causes discomfort, pain in the podkolennoy area. When considerable compresses the vessels and nerves, giving rise to a violation of the innervation and circulation of the blood.
- The disease of Goff – disease with the defeat and the rebirth of fatty tissue that extends around the joint of the knee. Crushing, swelling, and other damage in the fat cells of the adipocyte – end up replacing dense fibrous with a cloth. Finally, the indicator of the function of the "fat pillow" is in violation of itself in the adipose tissue is not capable of performing the function of a shock absorber.
- The disease of Osgood–Schlatter disease – pathology is characterized by necrosis bumpy part of the tibia. It is diagnosed in adolescents 10 to 18 years old participate in sporting activities. Below the kneecap appears painful bump, without treatment, leads to limitation of movement of the leg or the full immobilization, as well as the malnutrition of the muscles.
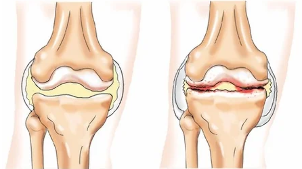
Of the disease, during which it is possible to irradiacin of pain in the knee area:
- Dysplastic hip – a chronicle of the defeat of the hip, hereditary, and progressive degeneration and degenerative changes in him. The pain often extends down the outer surface of the hip to the knee or below.
- Neuropathy of the sciatic nerve – not inflammatory the defeat of the nerve as a result of the compression of sinking or spazmirovannah of the blood vessels. This nerve reaches to the soles of the feet, beginning in the area of the waist and passing through the tail bone and the pelvis. The locking of a point along leads to the alteration of the sensitivity or throbbing pain.
- Fibromyalgia – extra-articular guided the defeat of the soft tissues non-inflammatory nature with a set of symptoms in the form of arthralgias, muscle weakness, depression, etc
Some systemic diseases that cause headaches in the knees:
- The treating osteoporosis is a bone disease chronic progressive of the current, which changes the mineral composition and bone density. "Washout" of calcium from the bones because of the fragility. The process is accompanied by the pain or the pain pains in the limbs.
- Tuberculosis of the bones. Tuberculosis is the defeat of the phase of bone leads to constant severe headaches.
- Osteomyelitis is a disease infectious-of an inflammatory nature that affects all the structural elements of the bones. The specific outcome such as, for example, tuberculosis, and nonspecific, more coccal, osteomyelitis becomes in the congestion of the skin, swelling of the local acute pain in the bones and muscles, feverish temperature.
- Some infectious diseases. In Reiter's syndrome, in addition to participation in the process of urogenitalnogo of the road and of the mucosa of the eyes, the affectation of the joints. One of the manifestations of lyme disease is arthralgia.
Types of pain in the knees
Depending on the etiology of the nature and intensity of the pain may be different.
- The pain. The case of arthritis, osteoarthritis.
- Sharp, strong. The crisis of the elements of the knee, torn ligaments, ostrom bursitis, knee injury, the exacerbation miniscope, deformation of the osteoarthritis.
- Throbbing. When running deformation, osteoarthritis, meniscal damage.
- Drill. When the osteomyelitis.
- Deaf. When the bursitis, chronic the Legg.
- Stinging. For the compression of the sciatic nerve, for the process in the bones.
- Shot. When jamming of the nerve trunk.
- The pain when walking. When baker's cyst, bursitis, arthritis, knee osteoarthritis, periarthritis.
- The pain at rest. In gout, arthritis.
The diagnosis of the pathologies that cause pain in the knees
Fizikalna survey:
- the collection of the medical history and complaints;
- visual inspection with palpation of the knee.
Laboratory studies:
- biochemical and clinical analysis of blood;
- serology the study of blood;
- immunological analysis of blood;
- rheumatology of the sample;
- bacteriological analysis of synovial fluid.
Invasive technical tools:
- arthroscopy;
- the puncture of the joint of bags;
- the puncture biopsy of bone.
It is a treatment non-invasive instrumental diagnostic:
- the x-ray of the knee;
- does the scan;
- ultrasound of the joint;
- The magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
Treatment of pain in the knees
If the pain in one or both knees non-traumatic nature of the appearance, you must first consult a therapist, who, on the basis of the patient's complaints and the hearing results of the inspection, and be directed to a narrow and specialist an orthopedic, a rheumatologist, taking into account or nevrologu. Any type of knee injury, you should consult a surgeon or orthopedist orthopedic.
The treatment in each case is different, depends on the cause of the pain, that is to say, the type of injury or disease. For each disease has its own treatment regimen. But, to begin with, the patient should follow some general rules:
- significantly reduce the life of the practice of trekking and to stay in the legs during the day;
- the athletes temporarily (until you recover) to waive the training, and the normal people of the race or jumps;
- the strengthening of the pain of renouncing completely to the movements, to impose on the knee, fixed the elastic band of the bandage;
- wear a bandage or dressing for immobilization of the knee;
- the bruised cold in place of trauma.
Rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, the autoimmune system of the disease need severe for the combined treatment of the school over many months. Percentage of the basic therapy consists of immunosuppressive drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and hormonal, medications, medications, gold, etc
In the treatment of bursitis using pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications. If they have identified the infection, treatment with antibiotics. The puncture bags is performed to remove the excess fluid from the synovial cavity and/or the introduction of one of the corticosteroids. Chronic inflammation of the bursa, helps to get rid of surgery is the surgical removal of synovial membrane of the bag.
When deformation of the osteoarthritis effective guided intra-articular injection corticosteroids, prolonged use of nsaids and chondroprotectors. To relieve the pain syndrome topically prescribed compresses with dimexide, or bischofite, ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory benefits. Help massage, physiotherapy, gymnastics. Serious injuries of the knee require surgical intervention – knee replacement.
The treatment of treating osteoporosis is course admission bisphosphonates, calcitonin, preparations of calcium, vitamin D, etc
Treatment of a meniscus tear can be conservative or surgical. Conservative treatment of consists in the application of analgesics, nsaids, hyaluronic acid, chondroprotectors. But at first produce reposition the joint.
Types of intervention:
- meniscectomy;
- partial (incomplete) meniscectomy;
- the transplantation of meniscus;
- arthroscopy;
- arthroscopic of the binding of a meniscus tear.
Any type of injury of the knee after treatment it is very important for the period of the rehabilitation, which must be carried out under the control of rehabilitation or an orthopedist. The doctor will be optimal for the program of recovery of the function of the joint. The main methods of post-operative rehabilitation are considered of massage and gymnastics. Are also effective the most important special classes, equipment, gradually develop the articulation of the knee.












































