Osteoarthritis (deformation of the osteoarthritis is a common name - the deposition of salts) is a chronic disease of the joints and on the other hand, degenerative nature, which produces the destruction of cartilage joint guidance, the capsule of the joint, the deformation of the bone.
It should be noted that osteoarthritis is a group of diseases of the joints, with different origins and loved ones of the mechanisms of development. Most often you find here the osteoarthritis of the major joints:
- deformation of the knee osteoarthritis (knee osteoarthritis),
- deforming osteoarthritis of the hip dysplastic),
- as well as osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
It is the heaviest of the types of osteoarthritis.
Arthrosis of the small joints of the less frequent. It is more common deformity osteoarthritis of interphalangeal joints of the hands, as well as the metacarpal-phalangeal joint big brush traces. Patients notice the pain in interphalangeal joints, decreased mobility, the emergence of near the joints of the joints (nodules Heberdena and Bouchard). This is the view of the arthrosis is more frequent in old age. Often the arthrosis of the joints of the feet.
The polyarthrosis, or generalized osteoarthritis, which is characterized by the defeat of several joints.
Osteoarthritis of the joints of the spine - spondiloarthrosis - belongs to the group of diseases of the spine, although it is similar to other degenerative disease development mechanism.
The main clinical symptom of osteoarthritis is pain in the joint, reducing your mobility. The specific symptoms are defined in the stage of the osteoarthritis and depend on the degree of destructive changes in the joint.
The causes of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is accepted divided into primary and secondary. Primary (idiopathic) osteoarthritis is the result of violation of processes of restoration and strengthening of the degeneration in the cartilage tissue of the joint, without any kind of deviations in the functioning of the whole organism. Secondary osteoarthritis occurs as a result of other pathological processes in the body, or in the already damaged of any external cause of the knee, with the partial destruction of the articular surfaces.
Often traumatic osteoarthritis is diagnosed in young patients. And in older patients, you can not always make a clear distinction between primary and secondary osteoarthritis).
Although the exact cause of osteoarthritis cannot be defined, the factors that favor the appearance and development, are well known.
We can distinguish the following types of causes that contribute to the development of primary and secondary deforming arthrosis.
The main cause of osteoarthritis - hereditary factors
We identified the following hereditary disorders of the violation, that may be the cause of the main development of osteoarthritis:
- genetic disorders in the composition of the cartilage of the joint, which leads to the acceleration of the destruction;
- congenital anomalies of the locomotor apparatus (hypermobility of the joints, dysplasia, flat feet and others), which are the cause of the mortality of the different sections of the cartilage tissue of the joint, and, as a consequence, the onset of osteoarthritis.
He also noted that deformation of the osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints of the upper limbs is found predominantly in women and is transmitted to the offspring by the female line.
Causes of the onset of secondary osteoarthritis
Secondary osteoarthritis is the result of injury of the joint. These damages can be caused by several factors.
- The mechanical damage of the joints. This group of factors include a variety of injuries of the joints, guided intra-articular fractures of bones, as a result of which alters the structure of the joint. To the same result leads to the constant of microfracture of the joints as a result of excessive loads, both static and dynamic (for example, athletes). Also the overhead and the traumatization of the joints leads to obesity.
Another factor that exerts a negative influence on the joints (especially the hip), is a poor posture.
The structure of the joint can also affect the surgery. - Diseases of the joints. Osteoarthritis may be a consequence of inflammatory diseases of the joints (acute and chronic arthritis, synovitis primary avascular necrosis of the bone etc)
- Metabolic disorders, diseases of the endocrine system, the deficiency of minerals in the body. Violations of exchange of substances, the lack of calcium, phosphorus and other minerals, vitamins and trace elements cause changes in the composition of the bone and the cartilage, synovial fluid, leading to the violation of the processes of restoration and the progressive destruction of the composition.
- Autoimmune diseases (to gout, chondrocalcinosis, hemochromatosis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis), hormonal disorders, estrogen deficiency after menopause in women cause changes in the tissues of the joints and gradual destruction.
- Vascular disease (atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, the destruction of the disease, varicose disease), as well as the physical inactivity, and cause problems with circulation in periarticular tissues, poor blood from the tissues of the joint and consequently dystrophic changes.
The mechanism of development of osteoarthritis
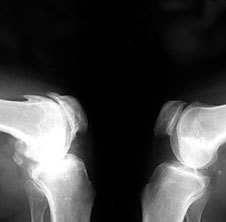
The development of osteoarthritis begins with the destruction of the cartilage. It is considered that in principle an infringement of the circulation of the blood in the capillaries Podhradie layer of periosteum. As well as the nutrition of the cartilage is produced by the absorption of the nutrients of the guided intra-articular fluid and adjacent bone, is the violation of the circulation of the blood causes the cartilage gradually loses its elasticity, becomes more thin, in it there are cracks, the smoothness of the joint surfaces is broken, it reduces the amount of synovial fluid, which provides a slip in the joint. Accordingly, it appears the pain and the popping in the movements. The width of the joint of the slit decreases gradually, at the edges of the articular surfaces is formed by bony spines-the osteophytes.
Eventually the joint becomes deformed, the amplitude of the movements in which he is reduced. Develops and involutive osteoarthritis, associated with the aging of the organism. The development of this form of osteoarthritis typically occurs slowly, over many years.
Other forms of osteoarthritis of the large joints, such as, for example, syndrome, post-infectious, metabolic, poisoning have different mechanisms of development, but the result is the same change in the joint.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis of the joints. In the stage and the grade of osteoarthritis
"Classic" is considered to be the classification of osteoarthritis based on the clinical and radiological characteristics of the signs. Under it there are three stages of development of the disease. It corresponds to the classification by the degree of conservation of the capacity for work, released 3 degree of osteoarthritis:
- I degree of osteoarthritis is a disease it does not prevent the execution of the work, though difficult to
- II degree of osteoarthritis is the disease prevents the execution of the work,
- Grade III osteoarthritis - the loss of ability to work.
We will consider the symptoms and clinical signs of osteoarthritis in each of the stages of the
Osteoarthritis of 1 degree (at the initial stage of arthrosis)
In the initial phase of the disease in the morning, after a rest, it is observed stiffness, difficulty of movement in the joints, which gradually passes through a time after the beginning of the movement. It is possible to a certain limitation of mobility, joint with guided. Periodically appear in the "initials" of pain (pain at the beginning of the movement after a long stay in the idle state). When sudden movements of the joint tingling, but the pain on motion does not exist. The pain in this stage of osteoarthritis appears only when the large and extended use of the load, and disappears after rest. At rest and in smaller loads pain does not exist. In this phase of the disease the patients rarely go to a doctor.
In the x-ray osteoarthritis grade 1 significant changes in the joint is not seen, sometimes you can see small osteophytes on the edges of the joint, the joint of the slit's a little bit of fill.
Osteoarthritis of degree 2 (the second phase of the arthritis)
For the development of osteoarthritis pain becomes substantial, acquires acute. Slight crack in the knee appears when any of the movements, there is a noteworthy limitation of the mobility joint guidance (contracture), functional shortening of the limbs, disorders of the biomechanics of the movements, but the mobility of the joint of the guard. In this stage is a notable feature of the initial gain of the pains become acute and prolonged. Under the influence of days of physical load, appears the constant tiredness, feeling of pressure in the affected joints, are produced the so-called "mechanical pain, caused by the decrease of the amortization of the capabilities the cartilage tissue of the joint.
The destruction of the articulation of the already quite significant, the joints are already partially deformed.
In the x-rays visible visible osteophytes, narrowing of joint cleft in 2-3 times in comparison with the norm, we observe multiple sclerosis, subchondral bone and the formation of cystic cavities in the epiphyseal area.
Osteoarthritis of degree 2 is characterized by the decrease of work capacity, the impossibility of the realization of some activities.
The osteoarthritis grade 3 (the third stage of osteoarthritis)
Osteoarthritis of the 3 degree - this is serious, it runs the phase of the disease. At this stage, we observe:
- a large deformation of the joint (due to the expansion of the bones and accumulation of fluid in the cavity articular guided);
- the drastic limitation of the movements, to the conservation of only a rocking of the movements;
- a sharp pain not only in the movement but in a state of complete peace - of persistent pain associated with reflex spasm of the nearby muscles, as well as the development of synovitis reactive;
- the inflammation of the joints
- the sensitivity of the joints to climate change.
- the muscles around the knee spasmatic atrophied;
The axis of the limb is misshapen, visibly varus or valgus bending of the legs (i.e., in the form of the letter "About" or "X").
In the x-rays osteoarthritis grade 3 it is observed the almost total disappearance of the joint of the slit, expressed in terms of the deformation of the articular surfaces, the vast multi-territorial osteophytes. You can define joint of the mouse and the calcification of para-articular tissues.
In 3 grade of the disease has gone too far, often because it is the cause of the permanent disability. It manifests itself in the following way:
- the pain becomes constant and painful: to walk, and especially the descent and the ascent of the stairs is a difficult time for the patient;
- a sharp crack in any direction of the movements, the well was able to listen to the associates;
- the deformation of the joints is very pronounced, the movement is limited to a small amplitude, or even impossible;
The images shows the destruction of the guided intra-articular (structures, ligaments and meniscus), as well as the wear and tear of the cartilage and signs of multiple sclerosis (replacement of the functioning of the organs and structures of connective tissue).
Osteoarthritis of the 4th grade
The state of complete destruction of the joint with osteoarthritis, when the joint completely and ceases to function, are often on your own - 4 degree of osteoarthritis. It is observed the so-called "locking the joint" - acute pain syndrome that, although the limited movement in the patient with surgery. The fourth level of the osteoarthritis is accompanied with unbearable pain in the joints that is not eliminated even potent analgesics and drugs intensive physiotherapy. Available complete ankylosis (fusion of joint) or newartriot (the education of the false joint between the biased ends of the bones). Independent of the circulation in both cases is practically impossible.
On the images visible hard multiple sclerosis soslanovna surfaces with cystic the lighting, the accumulation are joined to the bones in the area of the joint of the slit. The development of the disease before this stage, it almost always means the disability, to prevent that you can only implantation of artificial prosthetic joint.
The treatment of osteoarthritis
The treatment of osteoarthritis in the initial phase of the disease
Begin to heal osteoarthritis best as before, when the first signs - crackling in the joints, difficulty in movement. At this point, are useful drugs chondroprotectors, improve the structure of the cartilaginous tissue and vitamin-mineral complexes.
The importance of a therapeutic exercise, proper nutrition, as well as the implementation of preventive activities. It should be noted that the prevention of osteoarthritis is of great importance and to avoid a worsening of the disease.
The treatment of osteoarthritis of 2 - 3 grade
Despite cure osteoarthritis of 2-3 degrees because you can not, however, the process of their development can be visibly slow. Osteoarthritis treatment at this stage involves the following stages:
- removing or reducing the pain syndrome
- relieve the inflammation in the joint.
- to improve the recovery of cartilage tissue and slow down the degenerative processes of the of it.
In the period of acute treatment of osteoarthritis begins to address the pain. To do so, use non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids), analgesics. Are possible guided intra-articular injections of corticosteroids. It is necessary to reduce the load on the joint, in not too much time walking or standing, lifting heavy objects.
After the removal of the acute pain syndrome, the main challenge will be to ensure, to the extent possible, the activation of processes of restoration on the shoulder and periarticular tissues: improves blood circulation, improves the metabolism, elimination of inflammatory processes. Map chondroprotectors, vasodilator drugs, as well as gymnastics and physiotherapy.
The treatment of osteoarthritis of the 4th grade
In this phase of the disease of the joint, now almost completely destroyed. In this case, it is still an output of the operation, and the replacement of the joint of the patient stent-graft. Prosthesis significantly improves the mobility of the joint, allows you to resume an active life, as a minimum, by elimination of pain.












































